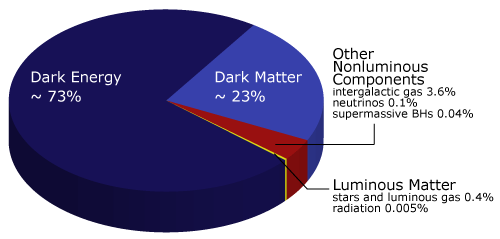
No matter how astrophysicists crunch the numbers, the universe simply doesn’t add up. Even though gravity is pulling inward on space-time — the “fabric” of the cosmos — it keeps expanding outward faster and faster. To account for this, astrophysicists have proposed an invisible agent that counteracts gravity by pushing space-time apart. They call it dark energy. In the most widely accepted model of dark energy, it is a “cosmological constant”: an inherent property of space itself, which has “negative pressure” driving space apart. As space expands, more space is created, and with it, more dark energy. Based on the observed rate of expansion, scientists know that the sum of all the dark energy must make up more than 70 percent of the total contents of the universe. But no one knows how to look for it. The best researchers have been able to do in recent years is narrow in a bit on where dark energy might be hiding, which was the topic of a study released in August 2015.

Fabulous
LikeLiked by 1 person